Efforts¶
The structures are designed to withstand external loads without deforming or breaking. As a consequence of these loads, structures experience internal forces called stresses.
Loads and efforts¶
- Burden
- External force acting on a structure. It can be a weight, a push, thermal expansion, etc.
- Effort
- Stress or internal force that appears in a structure as a result of external loads.
For example, a person sitting in a chair is a burden on the chair. Due to this load, the chair legs endure a compressive stress.
There are 5 types of efforts. Each one is explained below.
Traction¶
Tensile stress tends to stretch the structure:
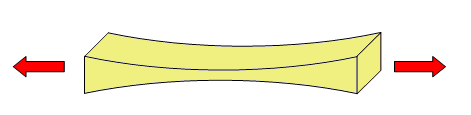
Examples of elements that support this effort:
- Chains of a swing.
- Crane cable.
Compression¶
The compressive stress tends to compress the structure:
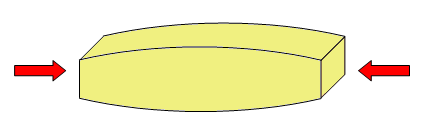
Examples of elements that support this effort:
- Legs of a chair.
- Columns of a building.
Flexion¶
The bending stress tends to bend the structure:
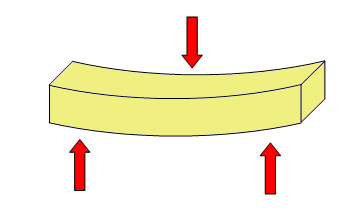
Examples of elements that support this effort:
- Board of a chair.
- Building floors.
- Crane arm.
Torsion¶
Torque tends to twist the structure:
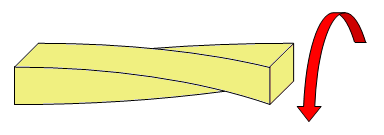
Examples of elements that support this effort:
- Shaft of a screwdriver.
- Key when turning.
- Axle of a tap.
Cutting or shearing¶
The shear or shear force tends to cut or slide one part of the structure with respect to the other:
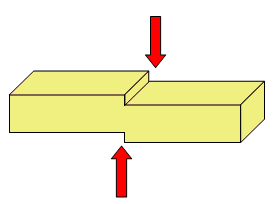
Examples of elements that support this effort:
- Paper cut with scissors.
- Horizontal beam that rests on a vertical beam.
- Screw that holds a painting.
Exercises¶
What is the difference between load and effort?
Write three examples of tensile stresses.
Write three examples of compressive stresses.
Write three examples of bending stresses.
Write three examples of torques.
Write three examples of shear stresses.
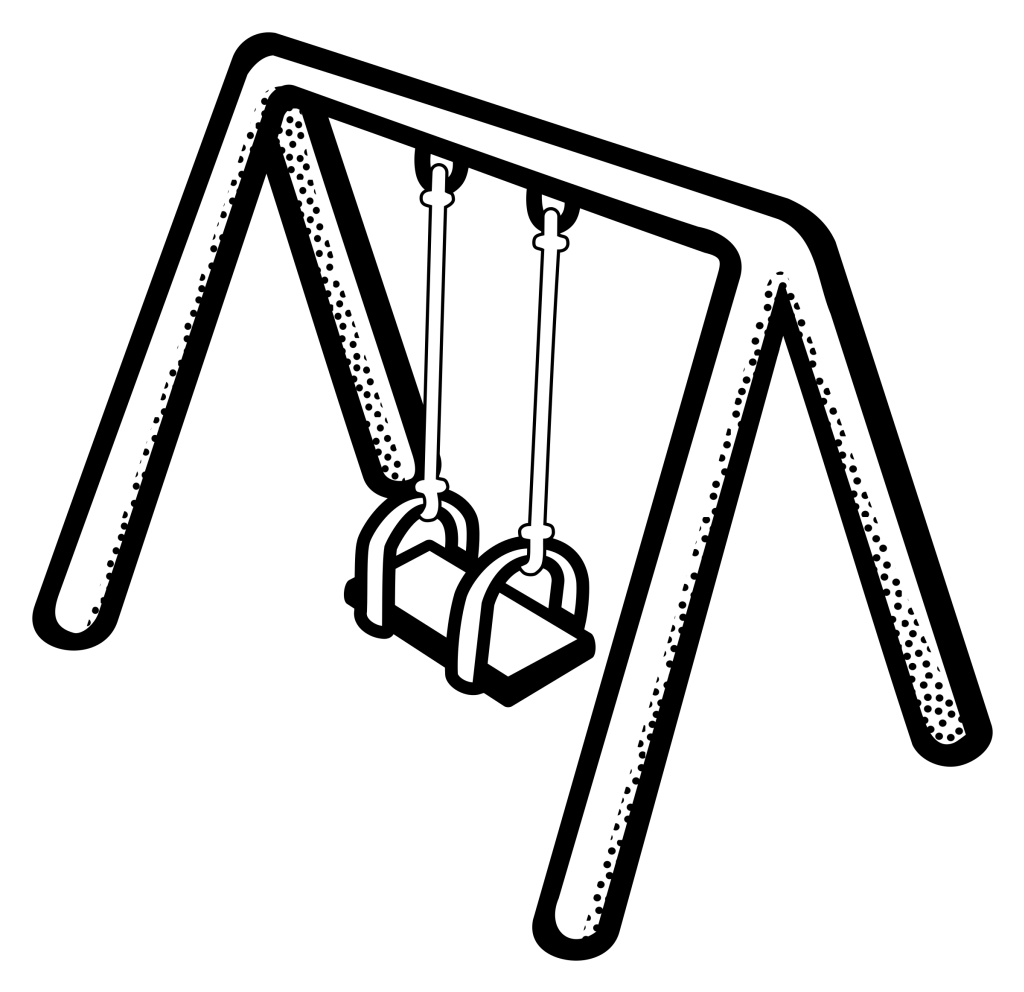
Draw and name the efforts that appear in a swing when a child climbs onto the seat.
Analyze the forces that appear on a table when a weight is placed on it.
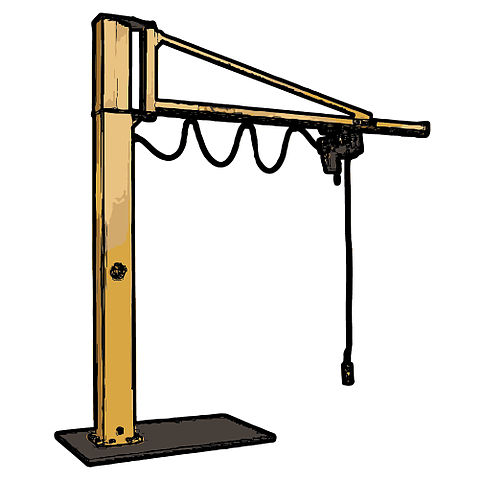
Analyze the forces that appear in the following crane when it lifts a load.
Unit test¶
Printable unit¶
Unit in printable format, with questions.