1. Digital signals¶
Until now, analog signals have been studied, which are voltage or current signals that can take any value within a range.
This is what an analog signal can look like:
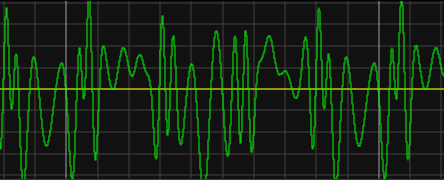
Example of analog signal.¶
Digital signals, on the other hand, are signals that only take discrete values, for example 0 volts and 5 volts. All other voltage values are ignored as invalid.
This is what a digital signal can look like with some noise added:
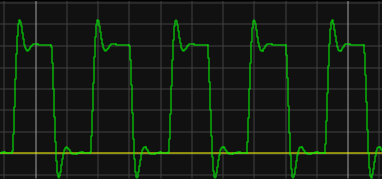
Example of a digital signal with added noise.¶
Digital signals can be converted to binary values and handle those binary numbers mathematically thanks to digital circuits. This provides many advantages to digital signals.
Advantages of digital signal¶
Immunity to noise.
Small value noise does not produce errors in the signal information.
Lossless duplication.
Digital signals can be duplicated without losing quality, because the noise that is introduced into the digital system can be eliminated.
Error detection and correction.
It can be calculated whether a digital signal has been degraded by noise (error detection) and any errors that have occurred can be corrected using mathematical techniques.
Ease of signal processing.
The digital signal can be easily processed with suitable software, which is capable of achieving more effects than analog processing. An example of this digital processing is the well-known Auto-Tune.
Digital quantification¶
Digital quantization is the process by which a signal is converted into binary values.
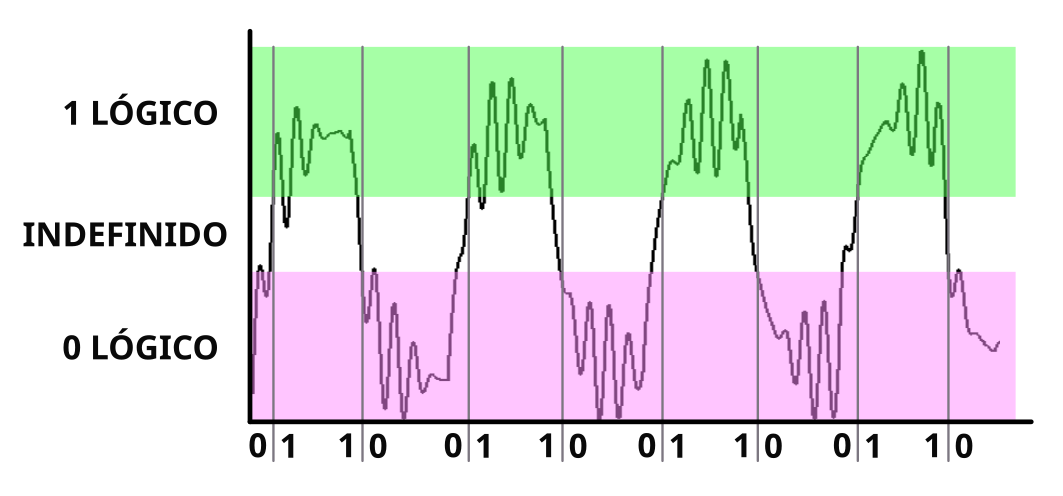
Definition of logical values in a noisy signal.¶
Simulation¶
Below you can see the simulation of a digital data signal with voltages between 0 and 5 volts, which deteriorates by adding noise in the transmission and which is finally recovered by eliminating the noise with a simple comparator with hysteresis (Trigger Schmitt). .
Exercises¶
Draw an analog signal and a digital signal.
How are they different?
What advantages do digital signals have?
What is digital quantification?
Explain in your words what happens in the simulated circuit.
Modify the FM signal in the simulator so that it has 3 volts maximum voltage. What happens to the recovered digital signal?
Draw the shape of the recovered digital signal and indicate the problem on the graph.